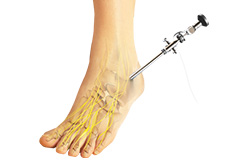
Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which an arthroscope, a small, soft, flexible tube with a light and video camera at the end, is inserted into the ankle joint to evaluate and treat a variety of conditions. The camera projects an image of the inside of the joint onto a large monitor, allowing your surgeon to look for any damage, assess the type of injury and repair the problem.
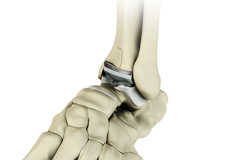
Ankle joint Replacement
Ankle joint replacement, also known as total ankle arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pain and immobility due to severe end-stage arthritis that has not responded to non-surgical treatments.
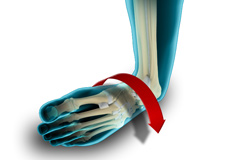
Ankle Instability Surgery
Ankle instability is a chronic condition characterized by the recurrent slipping of the outer side of the ankle. Instability is generally noticed during movement of the ankle joint, but can also occur while standing.
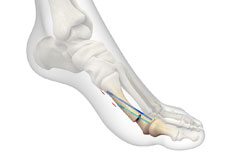
Minimally Invasive Bunion Surgery
Minimally invasive bunion surgery, also known as keyhole bunion surgery, is a procedure to treat a foot condition called a bunion or hallux valgus. During minimally invasive bunion surgery, a few small incisions are made to access the bone around the bunion, as opposed to a much larger incision made during an open bunion surgery that cuts across layers of tissue around the bone, causing more postoperative pain, a larger scar, and damage to the surrounding soft tissues.
Minimally Invasive Foot Surgery
Minimally invasive foot surgery (MIFS) uses the latest advanced technology to treat foot and ankle pain caused by a variety of conditions. Special surgical instruments, devices, and advanced imaging techniques are used to visualize and perform the surgery through small incisions. The aim of MIFS is to minimize damage to the muscles and surrounding structures, enabling a faster recovery with less pain.

Lesser Toe Surgery
Lesser toe surgery is an operation to correct deformities of the lesser toes other than the big toe. Some of the common lesser toe deformities include hammer toe, claw toe, and mallet toe.
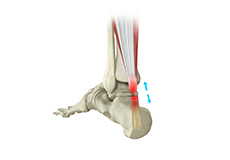
Achilles Tendon Rupture
The Achilles tendon is a strong fibrous cord present behind the ankle that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is used when you walk, run and jump.
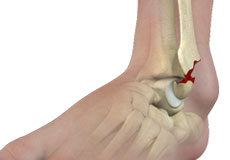
Ankle Fractures
Ankle injuries are very common in athletes and individuals performing physical work; often resulting in severe pain and impaired mobility.
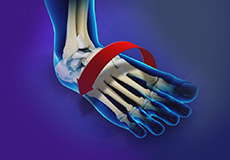
Ankle Instability
The joints of the ankle are held in place and stabilized by strong bands of tissue called ligaments. Ankle instability is a chronic condition characterized by a recurrent slipping of the outer side of the ankle.
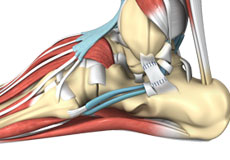
Ankle Sprain
A sprain is the stretching or tearing of ligaments. Ligaments connect adjacent bones and provide stability to a joint. An ankle sprain is a common injury that occurs when you suddenly fall or twist the ankle joint, or when you land your foot in an awkward position after a jump.
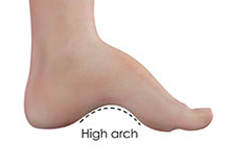
Cavus Foot Deformity
Cavus foot also referred to as a high arch, is a condition in which the arch on the bottom of the foot that runs from the toes to the heel is arched more than normal. Because of this, excessive weight falls on the ball and heel of the foot when walking or standing, causing pain and instability.
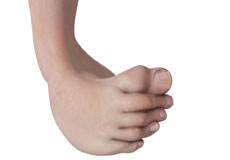
Congenital Vertical Talus
Talus is a small bone in your ankle joint. It sits between the heel bone (calcaneus) and the confluence of two bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula). Talus connects the lower leg to the foot to form the ankle and helps transfer weight across the ankle joint.
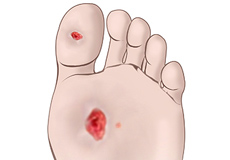
Diabetic Foot and Chronic Wounds
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose (sugar) levels. Diabetic patients are at high risk for developing chronic wounds, especially in the feet. If left untreated, these wounds can cause serious problems that can lead to infections and eventually gangrene, which may require amputation.
Flatfoot
Flatfoot, also known as “fallen arches” or Pes planus, is a deformity in children’s feet where the arch that runs along the sole of the foot collapses to the ground or is not formed at all. Flatfoot is normal in the first few years of life as the arch of the foot usually develops between the age of 3 and 5 years.

Common Toe Deformities
Lesser toe deformity is an abnormality in the anatomy of your toe that occurs as a result of imbalance between the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles.
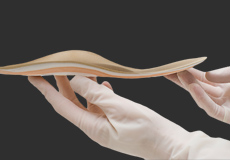
Orthotics and Assistive Devices
Foot orthotics also known as orthoses are specially designed supportive shoe inserts worn against the foot to relieve pain, provide protection, and treat foot or ankle deformities. They are available in multiple sizes and shapes to deliver prescription-based foot correction or may be custom-made with the help of a plaster cast or computer-aided 3D imaging of the foot.
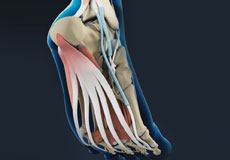
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis refers to the inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that is present at the bottom of the foot. It runs from the heel bone to the toes and forms the arch of your foot.
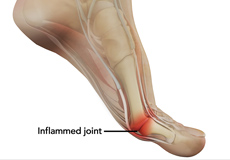
Turf Toe
Turf toe is an injury to the ligament at the base of the big toe. It is a painful condition that usually results from jamming the toe into the ground or excessive backward bending of the toe. As it is more common in athletes playing on artificial turf, especially those involved in field sports such as football, baseball, and soccer, it is known as turf toe.
What is the Normal Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle?
The foot and ankle form complex joints that are involved in movement and providing stability and balance to the body. The foot and ankle consist of 26 bones, 33 joints, and many muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Bones of the Ankle
The ankle joint connects the leg with the foot and is composed of three bones: the tibia, fibula, and talus. The tibia or shinbone and fibula or calf bone are bones of the lower leg, which articulate with the talus or ankle bone, enabling up and down movement of the foot.
Three bony bumps present on the ends of the tibia and fibula form parts of the ankle joint:
- The medial malleolus, formed by the tibia, is found on the inside of the ankle.
- The posterior malleolus, also formed by the tibia, is found at the back of the ankle.
- The lateral malleolus, formed by the fibula, is found on the outer aspect of the ankle.
Bones of the Feet
The foot acts as a single functional unit, but can be divided into three parts: the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot.
The hindfoot forms the ankle and heel, and is made up of the talus bone and calcaneus or heel bone. The heel bone is the largest bone in the foot.
The midfoot connects the hindfoot to the forefoot, and consists of one navicular bone, one cuboid bone, and three cuneiform bones. The navicular bone is found in front of the heel bone, and the cuneiform and cuboid bones are arranged in front of the navicular bone.
These bones are connected to five metatarsal bones of the forefoot that form the arch of the foot for shock absorption while walking or running. The forefoot is also made up of the toes or digits, formed by bones called phalanges - three in each toe, except the big toe, which has only two phalanges. The big toe has two additional tiny round sesamoid bones in the ball of the foot, which helps in upward and downward movements of the toe.
Ankle and Foot Joints
There are 33 joints in the ankle and foot. They include:
- Hinge joints in the ankle, which allow flexion (bending) and extension
- Gliding joints found in the hindfoot, which allow gliding movements
- Condyloid joints found in the forefoot and toes, which allow the flexion (bending) and extension, adduction, and abduction (sideward movement).
The joints of the foot and ankle provide stability and support the weight of your body, helping you to walk or run, and adapt to uneven grounds.
Soft Tissues of the Ankle and Foot
Our feet and ankle bones are held in place and supported by various soft tissues such as cartilage, ligaments, muscles, tendons, and bursae.
The joint surface of all the bones of the ankle and foot are lined by a thin, tough, flexible, and slippery surface called the articular cartilage, which acts as a shock absorber and cushion to reduce friction between the bones. The cartilage is lubricated by synovial fluid, which further enables smooth movement of the bones.
Ligaments are tough rope-like tissue that connect bones to other bones, and hold them in place, providing stability to the joints. The plantar fascia is the largest ligament in the foot, originating from the heel bone to the forefoot, it extends along the lower side of the foot and is involved in maintaining the arch of the foot. The plantar fascia ligament stretches and contracts to provide balance and strength to the foot. Lateral ligaments on the outside of the foot and medial ligaments on the inside of the foot provide stability and allow up and down movement of the foot.
The foot is made up of 20 muscles that help in movement. The main muscles include:
- Anterior tibial muscle, which allows up and down movement of the foot
- Posterior tibial muscle, which supports the arch
- Peroneal tibial muscle, which controls movement on the outside of the ankle
- Extensors, which enable the ankle to raise the toes just before stepping forward
- Flexors, which stabilize the toes against the floor
- Smaller muscles that help the toes to lift and curl
Tendons are soft tissues that connect muscles to bones. The largest and strongest tendon in the foot is the Achilles tendon, present at the back of the lower leg around the heel bone. Other tendons include peroneal and anterior and posterior tibialis.
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that decrease friction between tendons and bone or skin. They contain special cells called synovial cells that secrete a lubricating fluid.
 Online Bill Pay
Online Bill Pay Patient Portal
Patient Portal



